
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Diagnosis for Autism in Children is essential for early intervention. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects communication, behavior, and social interactions. It is called a ‘spectrum’ disorder because the symptoms and severity vary widely among individuals. Early detection and intervention play a crucial role in managing the condition effectively.
Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Recognizing autism spectrum disorder symptoms early can help in timely intervention. Some common signs in children include:
- Delayed speech or language skills
- Difficulty in maintaining eye contact
- Repetitive behaviors such as hand-flapping or rocking
- Lack of interest in social interactions
- Sensory sensitivities to lights, sounds, or textures
- Strong preference for routines and difficulty adapting to changes
- Difficulty understanding emotions and social cues
- Unusual reactions to the way things look, sound, smell, taste, or feel
If a child exhibits these symptoms persistently, parents should seek a professional evaluation for a formal diagnosis for autism.
Additional Indicators of ASD in Different Age Groups
Infants (Up to 12 Months)
- Limited or no response to their name
- Lack of social smiling
- Minimal eye contact
- Unusual reactions to sensory stimuli
Toddlers (1-3 Years)
- Delayed speech development
- Repetitive movements such as spinning, rocking, or hand-flapping
- Difficulty playing with peers or engaging in imaginative play
Preschool and School-Aged Children (4+ Years)
- Struggles with understanding jokes or figurative language
- Repetitive interests or intense focus on specific topics
- Difficulty adapting to new environments or changes in routine
- Challenges in understanding personal space and social norms
If a child exhibits these symptoms persistently, parents should seek a professional evaluation for a formal diagnosis for autism.
Diagnosis for Autism: Step-by-Step Process
1. Developmental Screening
Pediatricians usually conduct developmental screenings during regular checkups. These screenings assess speech, movement, and social behaviors. Parents may also be asked to complete questionnaires about their child’s behavior.
2. Comprehensive Diagnostic Evaluation
If the screening indicates potential autism spectrum disorder symptoms, a specialist, such as a developmental pediatrician, psychologist, or neurologist, performs an in-depth assessment. This evaluation includes:
- Behavioral observations
- Cognitive and language assessments
- Interviews with parents and caregivers
- Medical history review
- Hearing and vision tests to rule out other conditions
- Genetic testing to identify any underlying hereditary factors
3. Standardized Diagnostic Tools
Some of the widely used diagnostic tools include:
- Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS)
- Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS)
- Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT)
- Social Communication Questionnaire (SCQ)
- Gilliam Autism Rating Scale (GARS)
These tools help professionals confirm an accurate diagnosis for autism.

Nursing Diagnosis for Autism
A nursing diagnosis for autism focuses on identifying and addressing challenges faced by children with ASD. Some common nursing diagnoses include:
- Impaired social interaction
- Delayed communication development
- Sensory processing difficulties
- Risk of self-harm due to repetitive behaviors
- Ineffective coping mechanisms
- Risk of caregiver role strain
Nurses play a crucial role in autism spectrum disorder treatment by providing guidance to parents, ensuring behavioral support, and promoting individualized care plans.
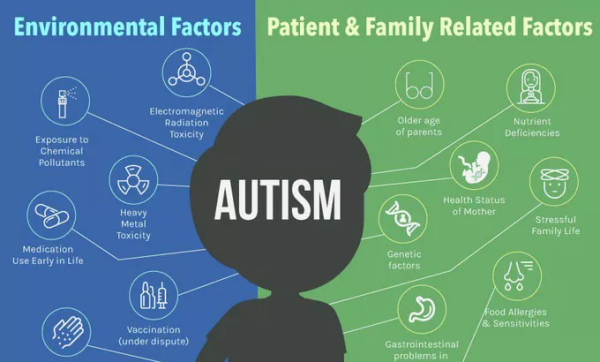
Causes of Autism Spectrum Disorder
While the exact causes of autism spectrum disorder are not fully understood, research suggests a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some potential causes include:
- Genetic mutations and family history
- Prenatal exposure to certain medications or infections
- Low birth weight or premature birth
- Environmental toxins
- Advanced parental age at conception
- Maternal metabolic conditions such as diabetes or obesity
- Brain structure and connectivity differences
Autism Spectrum Disorder Treatment
Although there is no cure for ASD, early intervention and therapy can significantly improve the quality of life for children with autism. Some effective treatment options include:
1. Behavioral Therapy
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is one of the most effective therapies that help children develop communication, social, and behavioral skills. Other behavioral interventions include:
- Early Start Denver Model (ESDM)
- Pivotal Response Treatment (PRT)
- Social Skills Training (SST)
2. Speech and Occupational Therapy
Speech therapy helps improve communication, while occupational therapy aids in developing motor skills and daily living abilities. Therapy may include:
- Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS)
- Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) devices
- Sensory integration techniques
3. Educational Support
Special education programs provide structured learning environments tailored to the child’s needs. Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) and 504 Plans ensure accommodations in schools for children with ASD.
4. Medication
Although no medication can cure ASD, certain medications help manage associated symptoms such as anxiety, hyperactivity, or aggression. Common medications include:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for anxiety and depression
- Stimulants for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)-like symptoms
- Antipsychotic drugs for severe behavioral issues
5. Parent and Family Training
Parental involvement is crucial in autism spectrum disorder treatment. Support groups, counseling, and parent training programs help families understand and manage ASD effectively.
6. Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Some families explore alternative therapies, including:
- Dietary interventions (gluten-free, casein-free diets)
- Omega-3 fatty acid supplements
- Music therapy
- Equine therapy (horse-assisted therapy)
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques

Conclusion
Early diagnosis for autism is essential for effective intervention and better developmental outcomes. Understanding autism spectrum disorder symptoms, causes of autism spectrum disorder, and available autism spectrum disorder treatment options can help parents and caregivers make informed decisions. At Nurturers, we provide comprehensive support and therapies tailored to meet the unique needs of each child on the spectrum.
If you suspect your child has ASD, seek professional guidance to ensure timely intervention and support. Early intervention leads to better progress and an improved quality of life for children with autism.

Hi! I am Swati Suri, a Special Educator with 9+ years of experience and the founder of Nurturers. I am passionate about helping children with special needs and supporting their families every step of the way.
Swati Suri
Special Educator | Founder, Nurturers

